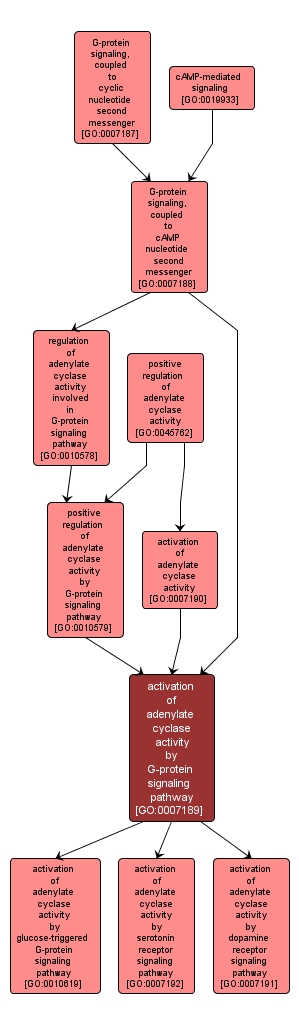
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
activation of adenylate cyclase activity by G-protein signaling pathway |
| Acc: |
GO:0007189 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that initiates the activity of an inactive adenylate cyclase that is an integral part of the series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, resulting in a subsequent change in the concentration of cyclic AMP. |
Synonyms:
- G-protein signaling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway
- GO:0010580
- G-protein signalling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway
- G-protein signalling, adenylyl cyclase activating pathway
- G protein signaling, adenylyl cyclase activating pathway
- G protein signalling, adenylyl cyclase activating pathway
- G protein signaling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway
- G-protein signaling, adenylyl cyclase activating pathway
- activation of adenylate cyclase activity involved in G-protein signaling
- G protein signalling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|