| Desc: |
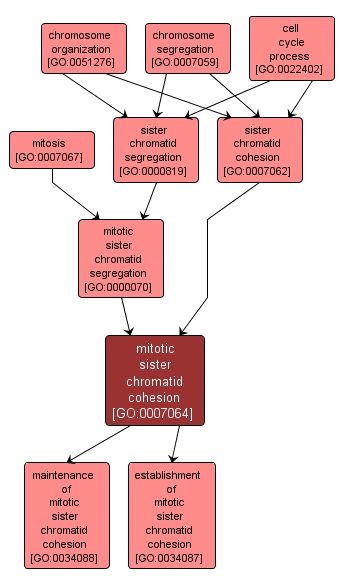
The cell cycle process whereby the sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome are joined along the entire length of the chromosome, from their formation in S phase through metaphase during a mitotic cell cycle. This cohesion cycle is critical for high fidelity chromosome transmission. |