GO TERM SUMMARY
|
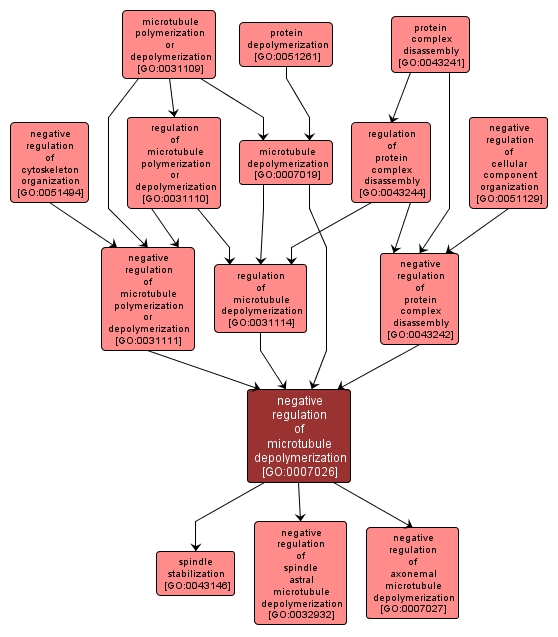
| Name: |
negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization |
| Acc: |
GO:0007026 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of microtubule depolymerization; prevention of depolymerization of a microtubule can result from binding by 'capping' at the plus end (e.g. by interaction with another cellular protein of structure) or by exposing microtubules to a stabilizing drug such as taxol. |
Synonyms:
- down regulation of microtubule depolymerization
- inhibition of microtubule depolymerization
- microtubule rescue
- negative regulation of microtubule catastrophe
- negative regulation of microtubule disassembly
- down-regulation of microtubule depolymerization
- downregulation of microtubule depolymerization
- microtubule stabilization
|