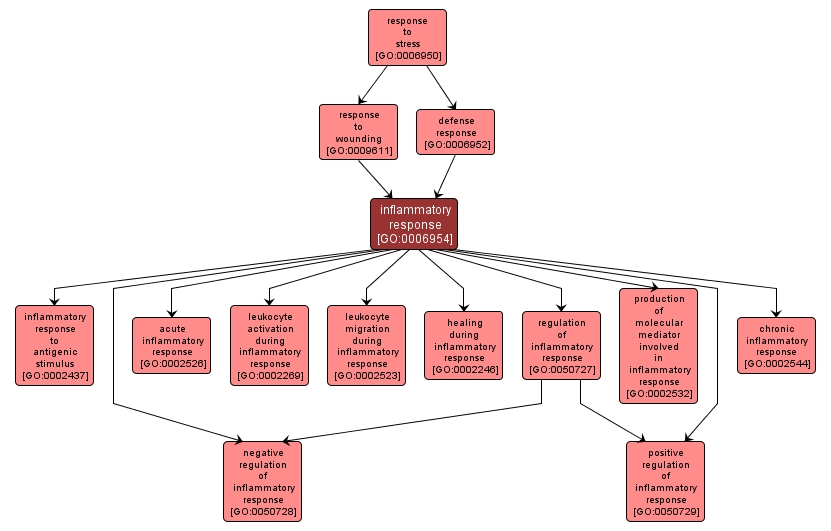
| Desc: |
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |