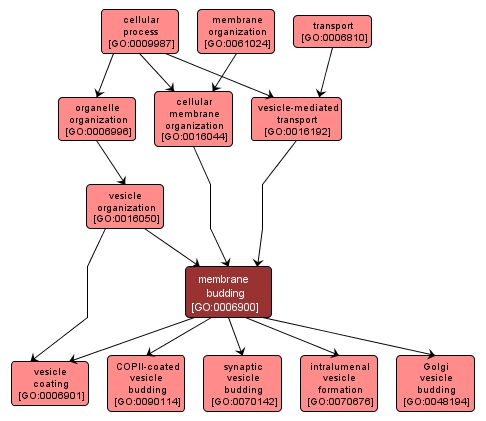
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
membrane budding |
| Acc: |
GO:0006900 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The evagination of a membrane, resulting in formation of a vesicle. |
Synonyms:
- membrane evagination
- GO:0006902
- vesicle biosynthesis
- vesicle formation
- nonselective vesicle assembly
- vesicle budding
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|