| Desc: |
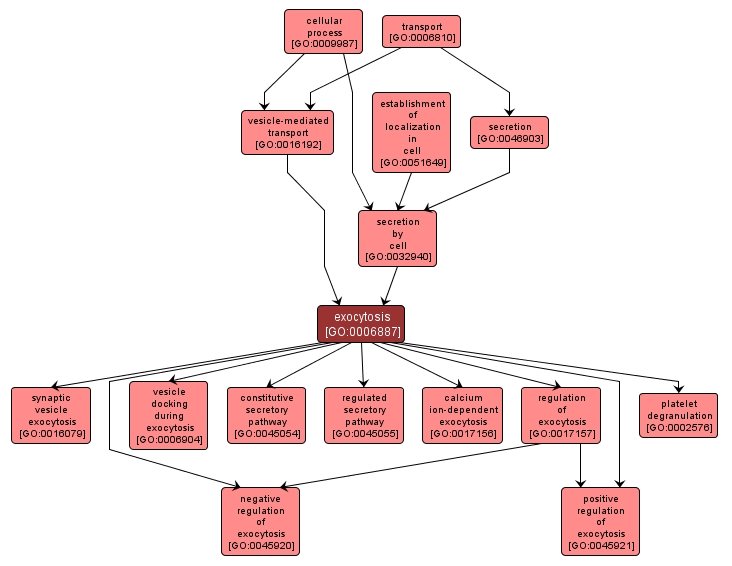
A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle by fusion of the vesicle with the plasma membrane of a cell. This is the process whereby most molecules are secreted from eukaryotic cells. |