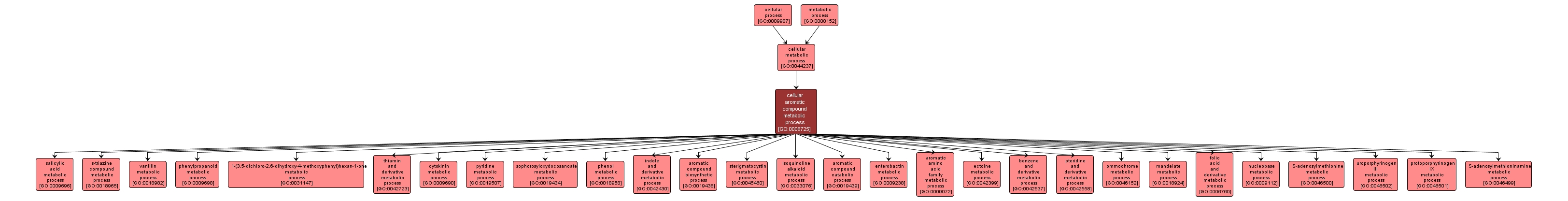
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular aromatic compound metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0006725 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic compounds, any organic compound characterized by one or more planar rings, each of which contains conjugated double bonds and delocalized pi electrons, as carried out by individual cells. |
Synonyms:
- aromatic compound metabolism
- aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism
- aromatic hydrocarbon metabolic process
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|