GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
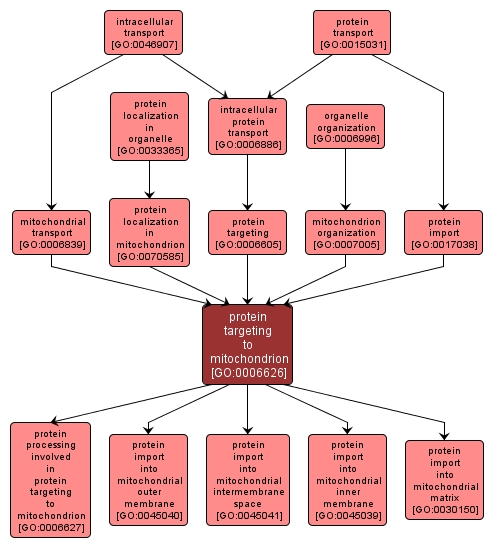
protein targeting to mitochondrion |
| Acc: |
GO:0006626 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process of directing proteins towards and into the mitochondrion, usually mediated by mitochondrial proteins that recognize signals contained within the imported protein. |
Synonyms:
- protein-mitochondrial targeting
- protein import into mitochondrion
- protein targeting to mitochondria
- GO:0043681
- mitochondrial protein import
- mitochondrial translocation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|