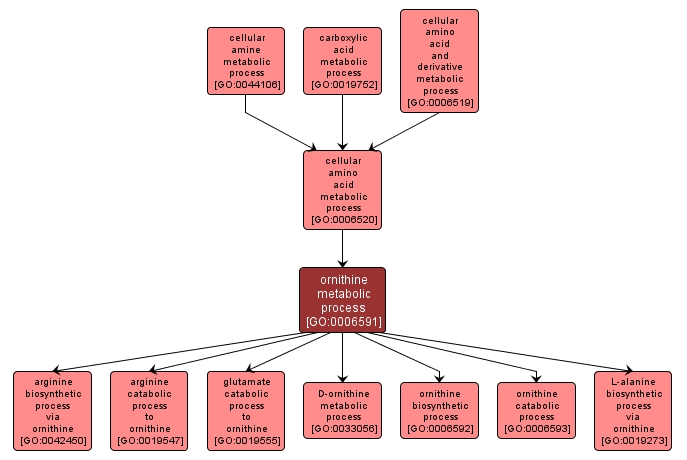
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ornithine metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0006591 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving ornithine, an amino acid only rarely found in proteins, but which is important in living organisms as an intermediate in the reactions of the urea cycle and in arginine biosynthesis. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|