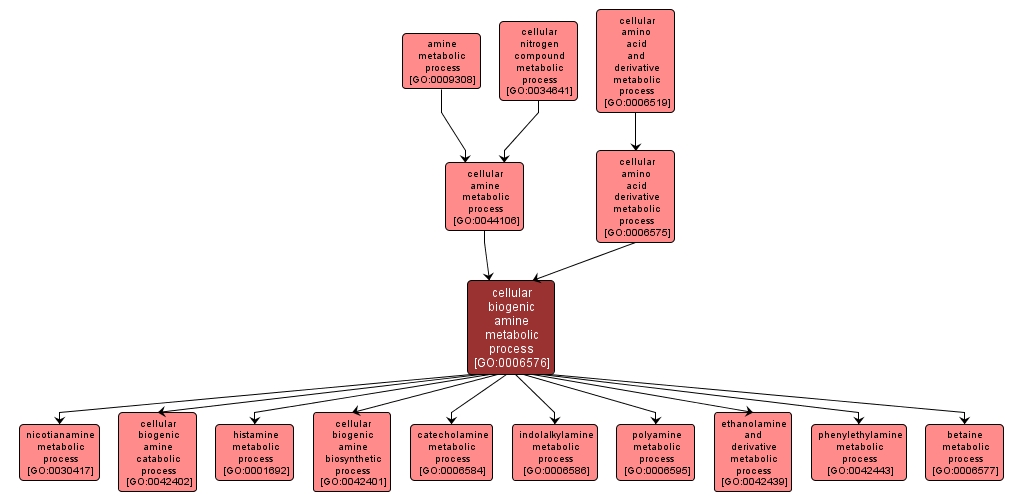
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters. |