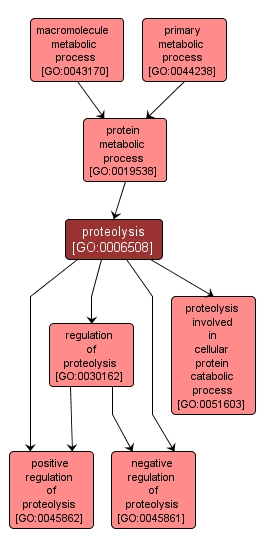
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
proteolysis |
| Acc: |
GO:0006508 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
Synonyms:
- peptidolysis
- ATP-dependent proteolysis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|