| Desc: |
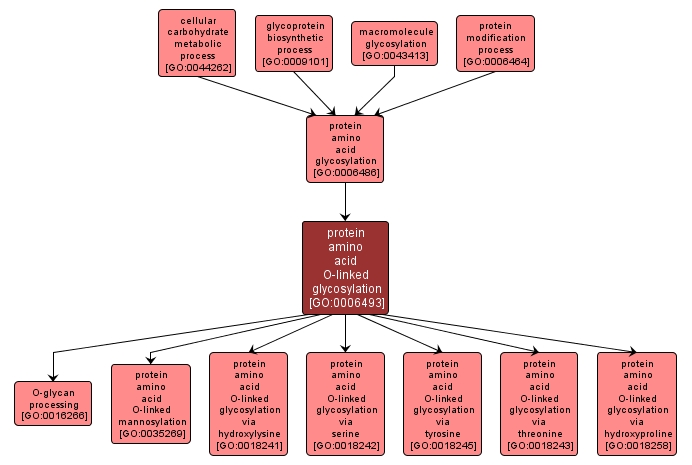
A protein amino acid glycosylation process in which a sugar unit is added to a protein via the hydroxyl group of peptidyl-serine, peptidyl-threonine, peptidyl-hydroxylysine, or peptidyl-hydroxyproline, or via the phenol group of peptidyl-tyrosine, forming an O-glycan. |