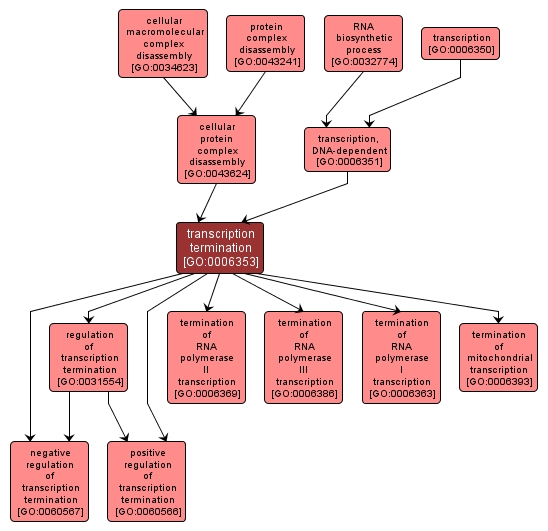
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
transcription termination |
| Acc: |
GO:0006353 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which transcription is completed; the formation of phosphodiester bonds ceases, the RNA-DNA hybrid dissociates, and RNA polymerase releases the DNA. |
Synonyms:
- transcriptional complex disassembly
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|