GO TERM SUMMARY
|
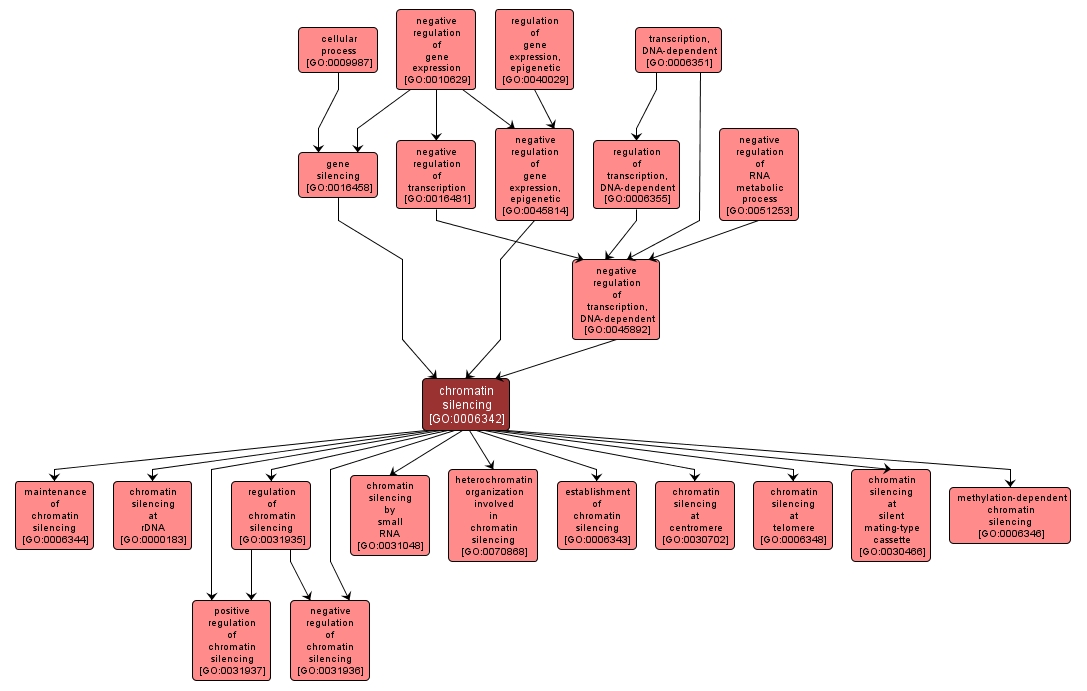
| Name: |
chromatin silencing |
| Acc: |
GO:0006342 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Repression of transcription by altering the structure of chromatin, e.g. by conversion of large regions of DNA into an inaccessible state often called heterochromatin. |
Synonyms:
- chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcriptional inactivation
- TGS
- chromatin-mediated silencing
- heterochromatic silencing
- transcriptional gene silencing
- GO:0016440
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|