| Desc: |
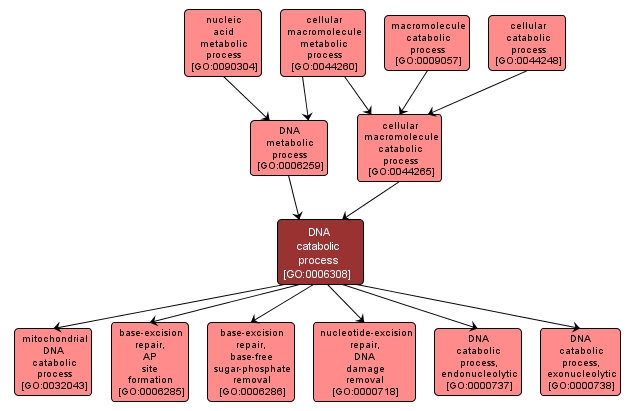
The cellular DNA metabolic process resulting in the breakdown of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long unbranched macromolecule formed from one or two strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides, the 3'-phosphate group of each constituent deoxyribonucleotide being joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage to the 5'-hydroxyl group of the deoxyribose moiety of the next one. |