| Desc: |
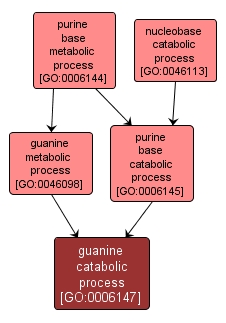
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of guanine, 2-amino-6-hydroxypurine, a purine that is one of the five main bases found in nucleic acids and a component of a number of phosphorylated guanosine derivatives whose metabolic or regulatory functions are important. |