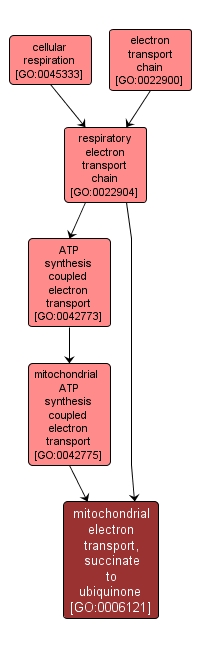
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
mitochondrial electron transport, succinate to ubiquinone |
| Acc: |
GO:0006121 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The transfer of electrons from succinate to ubiquinone that occurs during oxidative phosphorylation, mediated by the multisubunit enzyme known as complex II. |
Synonyms:
- oxidative phosphorylation, succinate to ubiquinone
- complex II (succinate to ubiquinone)
- mitochondrial electron transport, succinate to coenzyme Q
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|