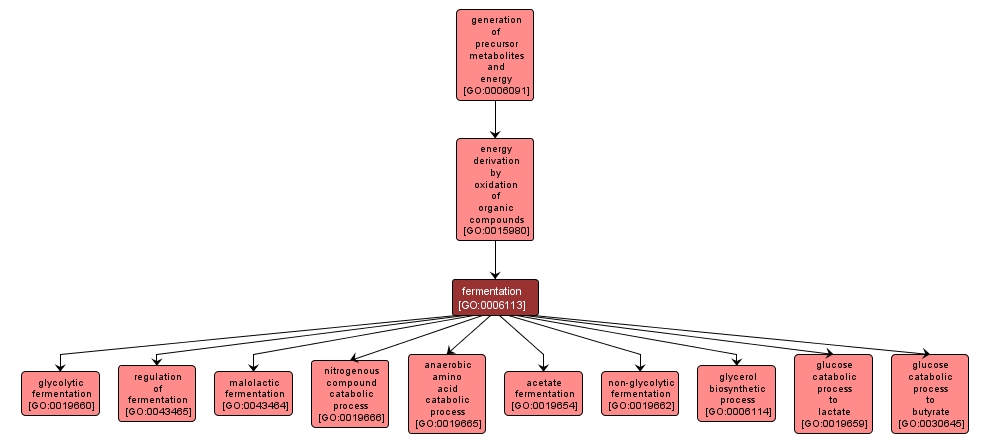
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
fermentation |
| Acc: |
GO:0006113 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The anaerobic enzymatic conversion of organic compounds, especially carbohydrates, to other compounds, especially to ethyl alcohol, yielding energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|