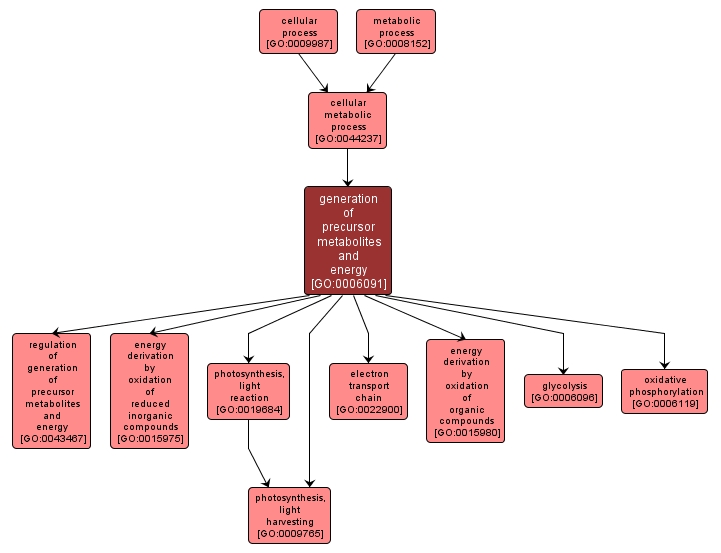
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
generation of precursor metabolites and energy |
| Acc: |
GO:0006091 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of precursor metabolites, substances from which energy is derived, and any process involved in the liberation of energy from these substances. |
Synonyms:
- metabolic energy generation
- energy pathways
- intermediary metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|