| Desc: |
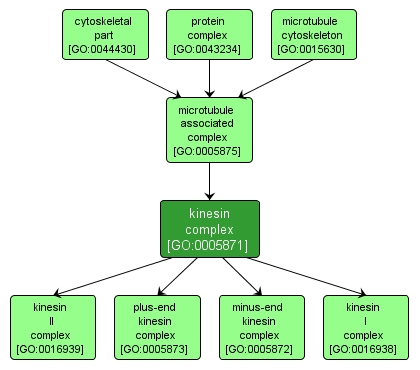
Any complex that includes a dimer of molecules from the kinesin superfamily, a group of related proteins that contain an extended region of predicted alpha-helical coiled coil in the main chain that likely produces dimerization. The native complexes of several kinesin family members have also been shown to contain additional peptides, often designated light chains as all of the noncatalytic subunits that are currently known are smaller than the chain that contains the motor unit. Kinesin complexes generally possess a force-generating enzymatic activity, or motor, which converts the free energy of the gamma phosphate bond of ATP into mechanical work. |