| Desc: |
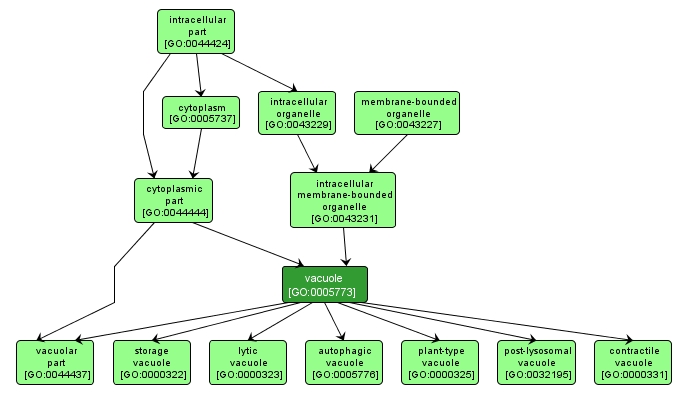
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol. |