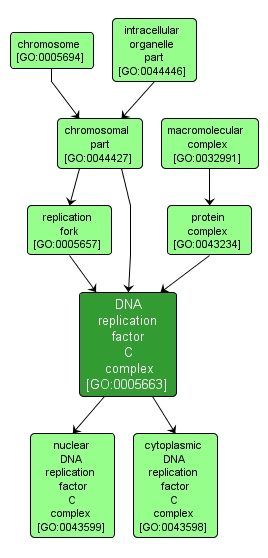
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
DNA replication factor C complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0005663 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A complex of five polypeptides in eukaryotes, and two in prokaryotes, that loads the DNA polymerase processivity factor proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) onto DNA, thereby permitting processive DNA synthesis catalyzed by DNA polymerase. |
Synonyms:
- activator 1 complex
- RFC complex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|