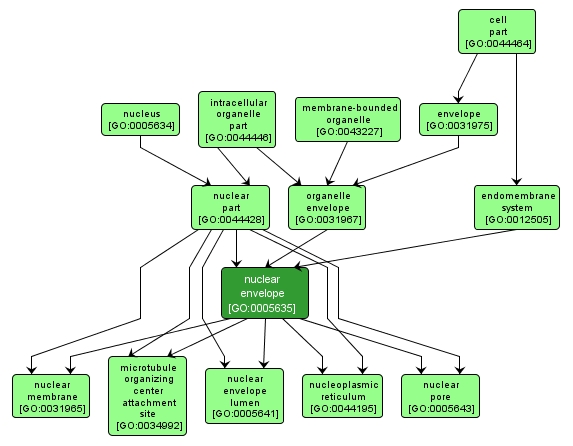
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
nuclear envelope |
| Acc: |
GO:0005635 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the nucleus and separating its contents from the rest of the cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space, a gap of width 20-40 nm (also called the perinuclear space). |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|