| Desc: |
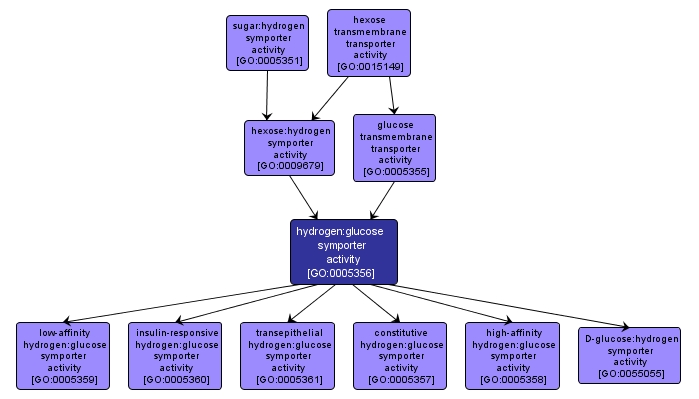
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: glucose + H+ = glucose + H+. Symporter activity enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy. |