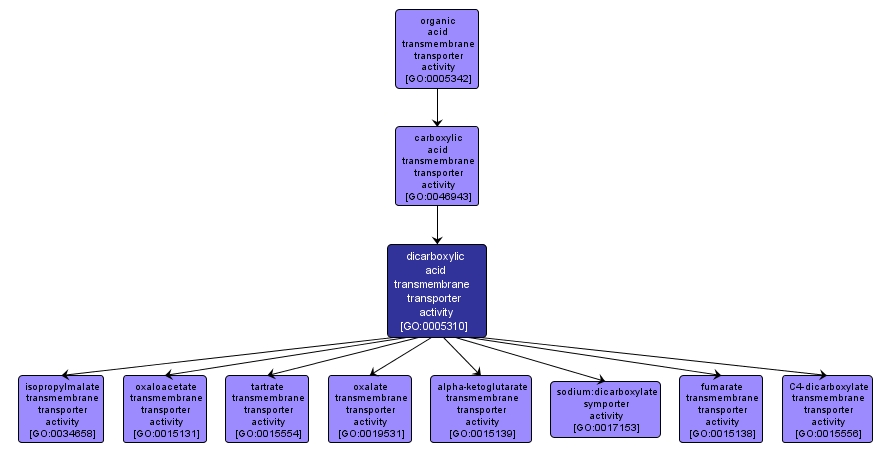
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
dicarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0005310 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of dicarboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic acid with two COOH groups. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0015365
- sodium:dicarboxylate/tricarboxylate symporter activity
- dicarboxylate carrier
- GO:0005312
- dicarboxylic acid permease activity
- dicarboxylate (succinate/fumarate/malate) antiporter activity
|