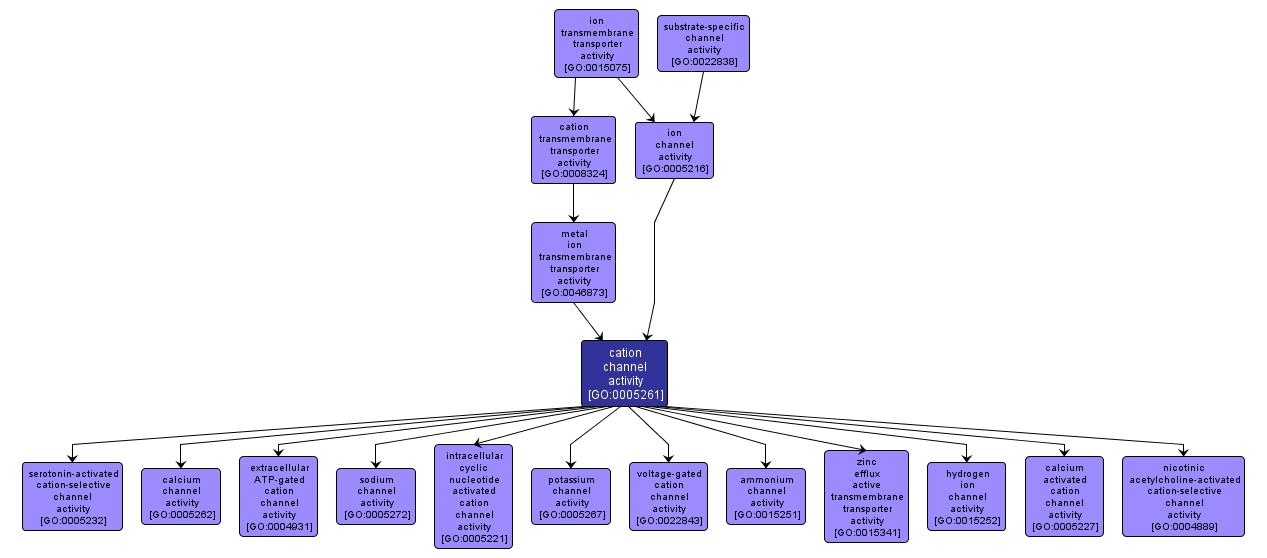
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cation channel activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0005261 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient. |
Synonyms:
- nonselective cation channel activity
- cation diffusion facilitator activity
- GO:0015281
- GO:0015338
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|