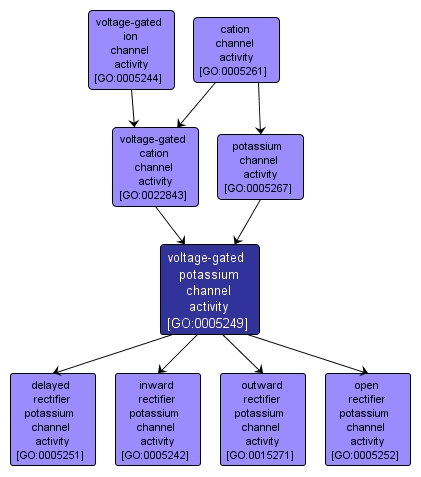
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
voltage-gated potassium channel activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0005249 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel. |
Synonyms:
- voltage-gated potassium ion channel activity
- voltage-dependent potassium channel activity
- voltage-sensitive potassium channel
- voltage gated potassium channel activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|