GO TERM SUMMARY
|
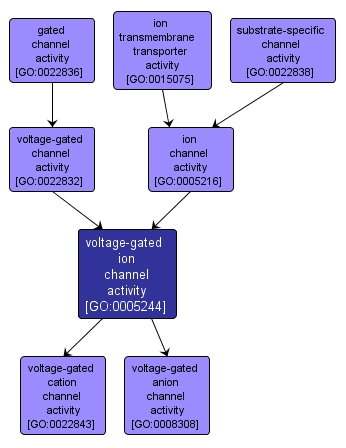
| Name: |
voltage-gated ion channel activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0005244 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons. |
Synonyms:
- voltage-dependent ion channel activity
- voltage gated ion channel activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|