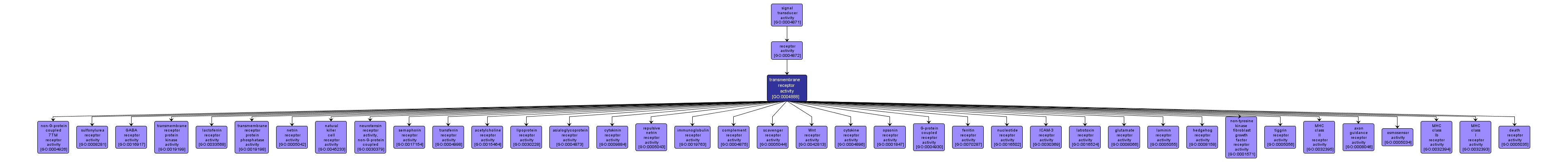
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
transmembrane receptor activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0004888 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|