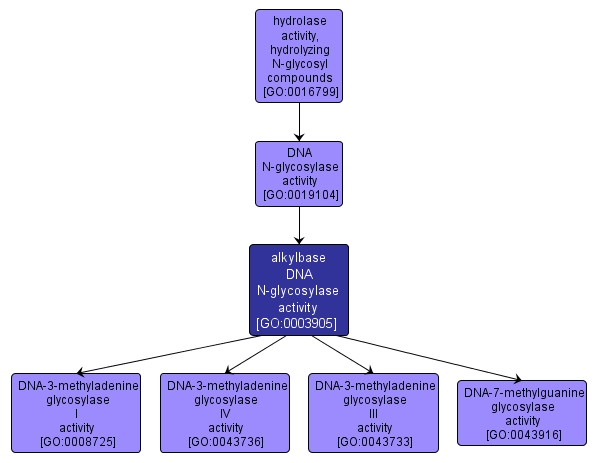
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
alkylbase DNA N-glycosylase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0003905 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of alkylated DNA; recognizes and removes alkylated purines and pyrimidines by cleaving the N-C1' glycosidic bond between the target damaged DNA base and the deoxyribose sugar. The reaction releases a free base and leaves an apurinic or apyrimidinic (AP) site. Enzyme has broad substrate specificity, being able to recognize alkylpurines, alkylpyrimidines or ethenopurines. |
Synonyms:
- 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase II
- deoxyribonucleate 3-methyladenine glycosidase II
- alkylated-DNA glycohydrolase (releasing methyladenine and methylguanine)
- DNA glycosidase II activity
- DNA-3-methyladenine glycosidase II activity
- DNA-3-methyladenine glycosylase II
- alkylbase DNA glycosidase activity
- GO:0004036
- AlkA
|