GO TERM SUMMARY
|
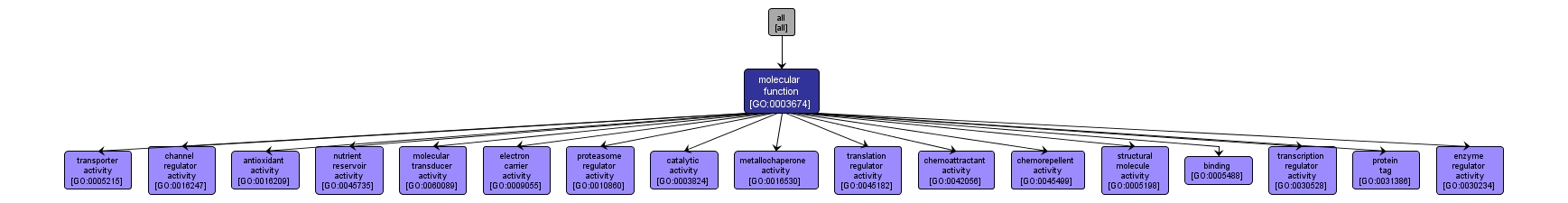
| Name: |
molecular_function |
| Acc: |
GO:0003674 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions. |
Synonyms:
- molecular function unknown
- molecular function
- GO:0005554
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|