GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
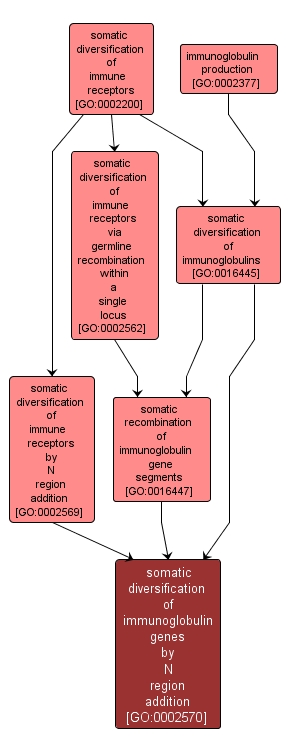
somatic diversification of immunoglobulin genes by N region addition |
| Acc: |
GO:0002570 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The addition of variable numbers of random nucleotides by terminal deoxytransferase in the N regions of heavy chain immunoglobulin genes. N regions are found at the V-D and D-J recombinational junctions. |
Synonyms:
- somatic diversification of antibody genes by N region addition
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|