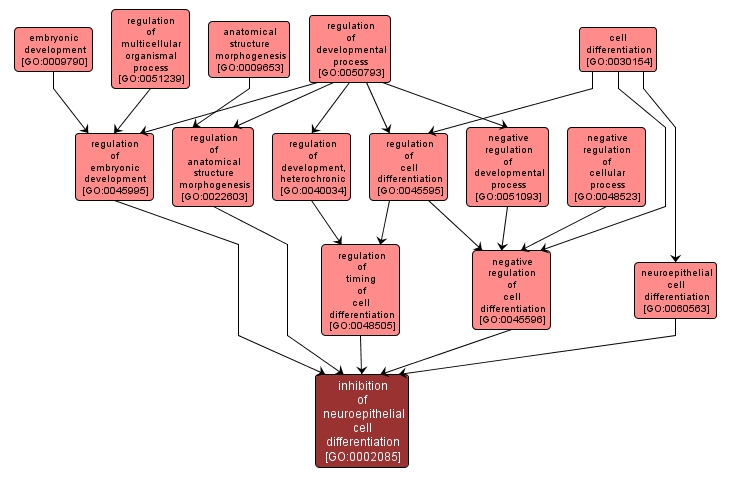
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
inhibition of neuroepithelial cell differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0002085 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that prevents the activation of neuroepithelial cell differentiation. Neuroepithelial cell differentiation is the process by which epiblast cells acquire specialized features of neuroepithelial cells. |
Synonyms:
- repression of premature neural plate formation
- negative regulation of neural plate formation
|