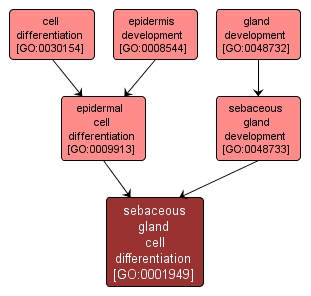
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
sebaceous gland cell differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0001949 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Process whereby a relatively unspecialized epidermal cell acquires the specialized features of a sebaceous gland cell. |
Synonyms:
- sebocytes differentiation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|