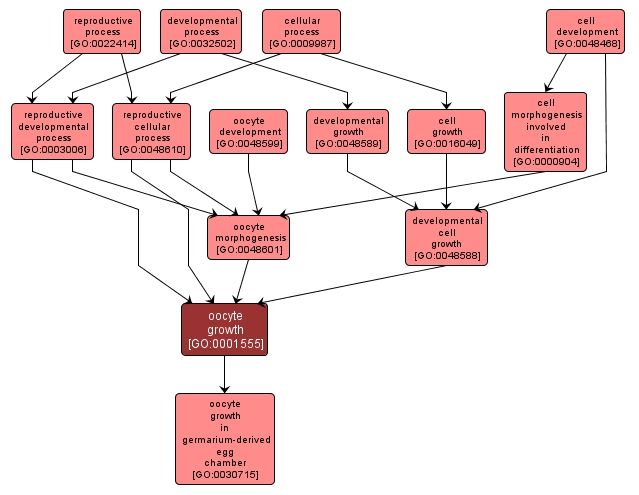
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
oocyte growth |
| Acc: |
GO:0001555 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which an oocyte irreversibly increases in size over time by accretion and biosynthetic production of matter similar to that already present. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|