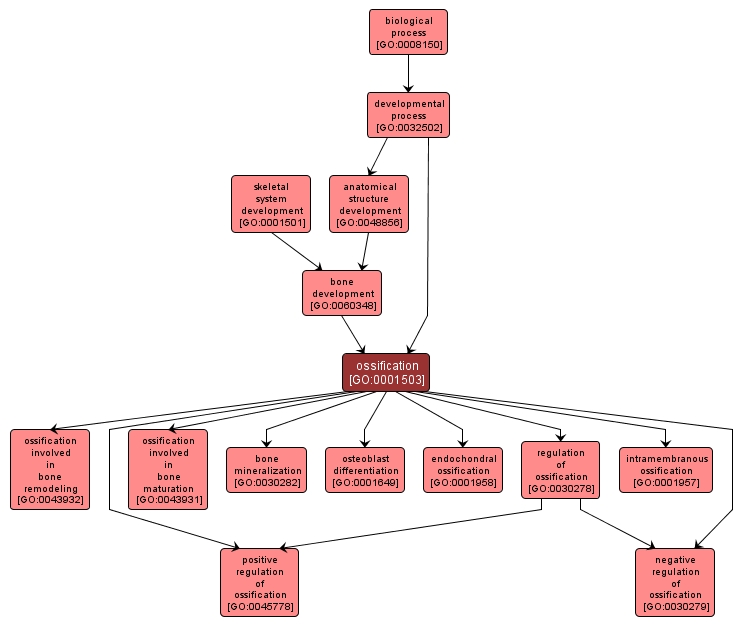
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ossification |
| Acc: |
GO:0001503 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance. |
Synonyms:
- bone biosynthesis
- bone formation
- osteogenesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|