| Desc: |
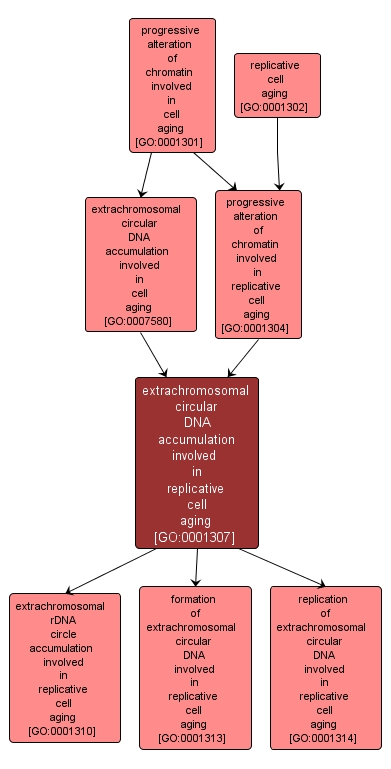
Increase in abundance of circular DNA molecules in dividing cells as they age. These molecules originate in the chromosome but are excised and circularized, often by intramolecular homologous recombination between direct tandem repeats, and then replicated independently of chromosomal replication. |