GO TERM SUMMARY
|
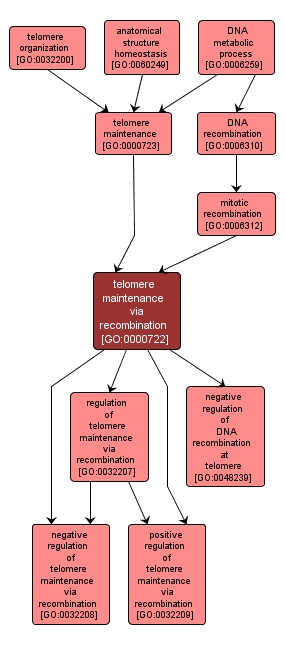
| Name: |
telomere maintenance via recombination |
| Acc: |
GO:0000722 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any recombinational process that contributes to the maintenance of proper telomeric length. |
Synonyms:
- telomerase-independent telomere maintenance
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|