| Desc: |
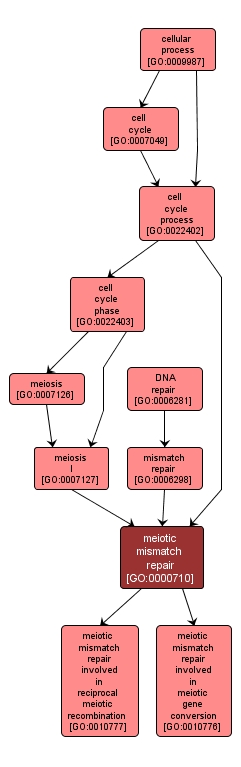
A system for the identification and correction of base-base mismatches, small insertion-deletion loops, and regions of heterology that are present in duplex DNA formed with strands from two recombining molecules. Correction of the mismatch can result in non-Mendelian segregation of alleles following meiosis. |