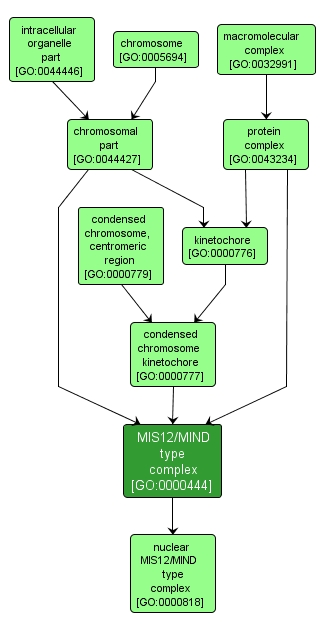
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
MIS12/MIND type complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0000444 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A multiprotein kinetochore subcomplex that binds to centromeric chromatin and forms part of the inner kinetochore. It helps to recruit outer kinetochore subunits that will bind to microtubules. In humans, it consists of MIS12, DSN1, NSL1 and PMF1. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|