GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
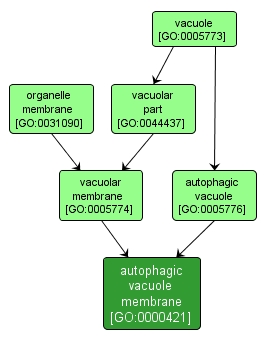
autophagic vacuole membrane |
| Acc: |
GO:0000421 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The lipid bilayer surrounding an autophagic vacuole, a double-membrane-bounded vesicle in which endogenous cellular material is sequestered. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|