GO TERM SUMMARY
|
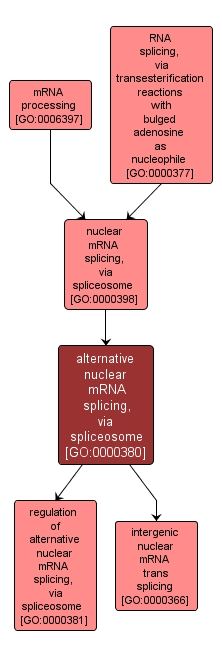
| Name: |
alternative nuclear mRNA splicing, via spliceosome |
| Acc: |
GO:0000380 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process of generating multiple mRNA molecules from a given set of exons by differential use of exons from the primary transcript(s) to form multiple mature mRNAs that vary in their exon composition. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|