GO TERM SUMMARY
|
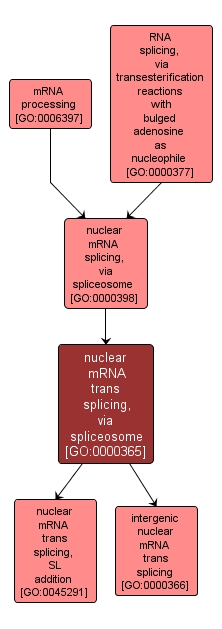
| Name: |
nuclear mRNA trans splicing, via spliceosome |
| Acc: |
GO:0000365 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The joining together of exons from two different primary transcripts of messenger RNA (mRNA) via a spliceosomal mechanism, so that mRNA consisting only of the joined exons is produced. |
Synonyms:
- nuclear mRNA trans splicing, via U2-type spliceosome
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|