GO TERM SUMMARY
|
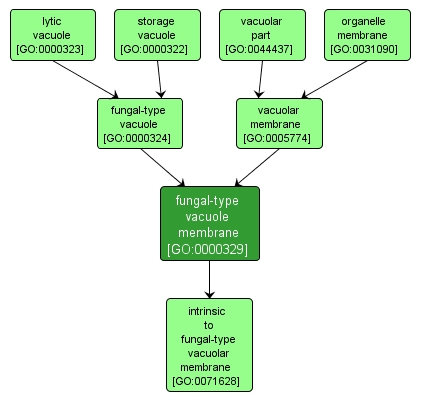
| Name: |
fungal-type vacuole membrane |
| Acc: |
GO:0000329 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The lipid bilayer surrounding a vacuole, the shape of which correlates with cell cycle phase. The membrane separates its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell. An example of this structure is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
Synonyms:
- fungal-type vacuolar membrane
- membrane of vacuole with cell cycle-correlated morphology
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|