GO TERM SUMMARY
|
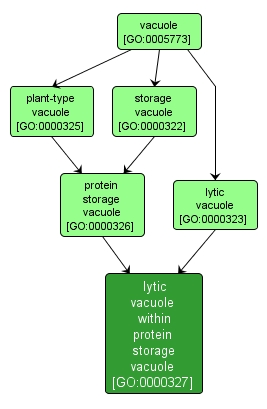
| Name: |
lytic vacuole within protein storage vacuole |
| Acc: |
GO:0000327 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A membrane-bounded compartment containing crystals of phytic acid and proteins characteristic of a lytic vacuole, found within a storage vacuole. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|