GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
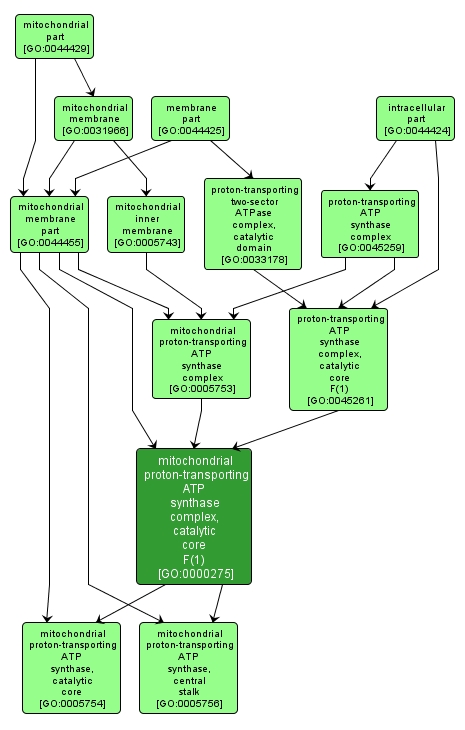
mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1) |
| Acc: |
GO:0000275 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The catalytic sector of the mitochondrial hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase; it comprises the catalytic core and central stalk, and is peripherally associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane when the entire ATP synthase is assembled. |
Synonyms:
- hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase, F1 sector
- proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1)
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|