GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
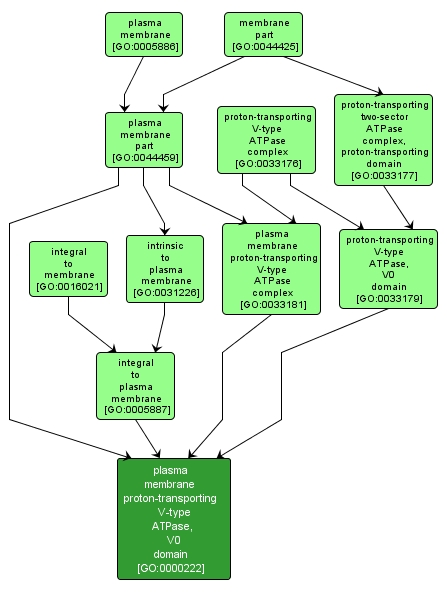
plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain |
| Acc: |
GO:0000222 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The V0 domain of a proton-transporting V-type ATPase found in the plasma membrane. |
Synonyms:
- plasma membrane hydrogen ion-transporting ATPase V0 domain
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|