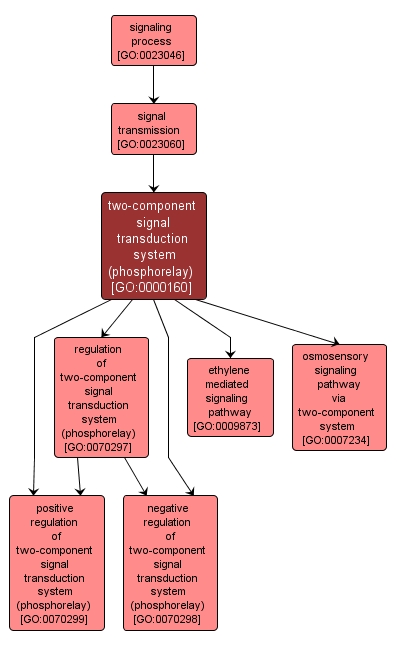
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
two-component signal transduction system (phosphorelay) |
| Acc: |
GO:0000160 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A conserved series of molecular signals found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes; involves autophosphorylation of a histidine kinase and the transfer of the phosphate group to an aspartate that then acts as a phospho-donor to response regulator proteins. |
Synonyms:
- histidyl-aspartyl phosphorelay
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|