| Desc: |
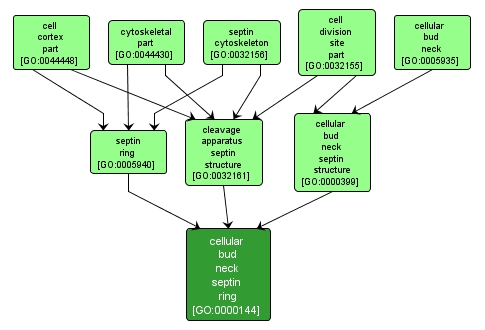
A ring-shaped structure that forms at the site of cytokinesis; composed of members of the conserved family of filament forming proteins called septins as well as septin-associated proteins. In S. cerevisiae, this structure forms at the time of bud emergence and the septins show a high rate of exchange. |