| Desc: |
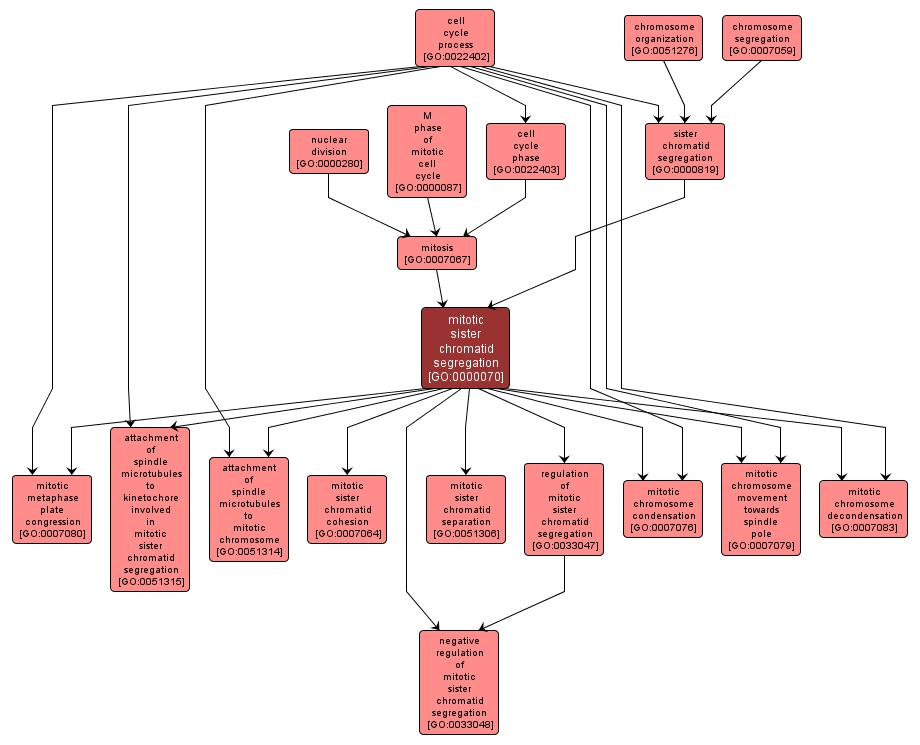
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets. |